Difference between revisions of "Chain of command"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:lighterstill.jpg]][[File:MFD_Ranks2.jpg|right|frame]] | [[File:lighterstill.jpg]][[File:MFD_Ranks2.jpg|right|frame]] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/19th_century 1898] |
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
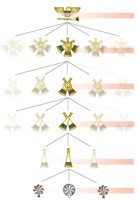
*1: a [[series]] of positions of [[military]] or civil [[authority]] such that each holder is directly [[responsible]] to, and takes his orders from, the next above. | *1: a [[series]] of positions of [[military]] or civil [[authority]] such that each holder is directly [[responsible]] to, and takes his orders from, the next above. | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | In a [[military]] [[context]], the '''chain of command''' is the line of [[authority]] and responsibility along which orders are passed within a military unit and between different units. Orders are [[transmitted]] down the chain of command, from a higher-ranked [[soldier]], such as a [ | + | In a [[military]] [[context]], the '''chain of command''' is the line of [[authority]] and responsibility along which orders are passed within a military unit and between different units. Orders are [[transmitted]] down the chain of command, from a higher-ranked [[soldier]], such as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commissioned_officer commissioned officer], to lower-ranked personnel who either execute the order personally or transmit it down the chain as appropriate, until it is received by those [[expected]] to [[execute]] it. |
In general, [[military]] personnel give orders only to those directly below them in the ''chain of command'' and receive orders only from those directly above them. A service member who has [[difficulty]] executing a [[duty]] or order and appeals for relief directly to an officer above his immediate commander in the chain of command is likely to be [[disciplined]] for not observing the chain of command. Similarly, an officer is usually [[expected]] to give orders only to his or her direct subordinate, even if it is just to pass an order down to another service member lower in the chain of command than said subordinate. | In general, [[military]] personnel give orders only to those directly below them in the ''chain of command'' and receive orders only from those directly above them. A service member who has [[difficulty]] executing a [[duty]] or order and appeals for relief directly to an officer above his immediate commander in the chain of command is likely to be [[disciplined]] for not observing the chain of command. Similarly, an officer is usually [[expected]] to give orders only to his or her direct subordinate, even if it is just to pass an order down to another service member lower in the chain of command than said subordinate. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The concept of chain of command also implies that higher rank alone does not entitle a higher-ranking service member to give commands to anyone of lower rank. For example, an officer of unit "A" does not directly command lower-ranking members of unit "B", and is generally [[expected]] to approach an officer of unit "B" if he requires [[action]] by members of that unit. The chain of command means that [[individual]] members take orders from only one superior and only give orders to a defined group of people [[immediately]] below them. | The concept of chain of command also implies that higher rank alone does not entitle a higher-ranking service member to give commands to anyone of lower rank. For example, an officer of unit "A" does not directly command lower-ranking members of unit "B", and is generally [[expected]] to approach an officer of unit "B" if he requires [[action]] by members of that unit. The chain of command means that [[individual]] members take orders from only one superior and only give orders to a defined group of people [[immediately]] below them. | ||
| − | If an officer of unit "A" does give orders directly to a lower-ranked member of unit "B", it would be [[considered]] highly [[unusual]] (a [ | + | If an officer of unit "A" does give orders directly to a lower-ranked member of unit "B", it would be [[considered]] highly [[unusual]] (a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faux_pas faux pas]) as officer "A" would be seen as subverting the [[authority]] of the officer of unit "B". Depending on the situation or the standard [[procedure]] of the [[military]] [[organization]], the lower-ranked member being ordered may [[choose]] to carry out the order anyway, or advise that it has to be cleared with his or her own ''chain of command'' first, which in this example would be with officer "B". Refusal to carry out an order is almost always considered insubordination, the only exception usually allowed is if the order itself is illegal (i.e., the person carrying out the order would be committing an [[Crime|illegal act]]). (See [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superior_Orders Superior Orders].) |
| − | In addition, within [ | + | In addition, within [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combat combat] units, line officers are in the ''chain of command'', but officers in specialist fields (such as [[medical]], dental, [[legal]], supply, and chaplain) are not, except within their own specialty. For example, a [[medical]] officer in an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infantry infantry] battalion would be [[responsible]] for the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combat_medics combat medics] in that unit but would not be eligible to command the battalion or any of its subordinate units. |
| − | The term is also used in a [ | + | The term is also used in a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Civilian civilian] management [[context]] describing comparable [[hierarchical]] [[structures]] of [[authority]]. |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:45, 12 December 2020
Definitions
- 1: a series of positions of military or civil authority such that each holder is directly responsible to, and takes his orders from, the next above.
Description
In a military context, the chain of command is the line of authority and responsibility along which orders are passed within a military unit and between different units. Orders are transmitted down the chain of command, from a higher-ranked soldier, such as a commissioned officer, to lower-ranked personnel who either execute the order personally or transmit it down the chain as appropriate, until it is received by those expected to execute it.
In general, military personnel give orders only to those directly below them in the chain of command and receive orders only from those directly above them. A service member who has difficulty executing a duty or order and appeals for relief directly to an officer above his immediate commander in the chain of command is likely to be disciplined for not observing the chain of command. Similarly, an officer is usually expected to give orders only to his or her direct subordinate, even if it is just to pass an order down to another service member lower in the chain of command than said subordinate.
The concept of chain of command also implies that higher rank alone does not entitle a higher-ranking service member to give commands to anyone of lower rank. For example, an officer of unit "A" does not directly command lower-ranking members of unit "B", and is generally expected to approach an officer of unit "B" if he requires action by members of that unit. The chain of command means that individual members take orders from only one superior and only give orders to a defined group of people immediately below them.
If an officer of unit "A" does give orders directly to a lower-ranked member of unit "B", it would be considered highly unusual (a faux pas) as officer "A" would be seen as subverting the authority of the officer of unit "B". Depending on the situation or the standard procedure of the military organization, the lower-ranked member being ordered may choose to carry out the order anyway, or advise that it has to be cleared with his or her own chain of command first, which in this example would be with officer "B". Refusal to carry out an order is almost always considered insubordination, the only exception usually allowed is if the order itself is illegal (i.e., the person carrying out the order would be committing an illegal act). (See Superior Orders.)
In addition, within combat units, line officers are in the chain of command, but officers in specialist fields (such as medical, dental, legal, supply, and chaplain) are not, except within their own specialty. For example, a medical officer in an infantry battalion would be responsible for the combat medics in that unit but would not be eligible to command the battalion or any of its subordinate units.
The term is also used in a civilian management context describing comparable hierarchical structures of authority.