Difference between revisions of "Unit"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
For example, length is a physical quantity. The metre is a unit of length that [[represents]] a definite predetermined length. When we say 10 metres (or 10 m), we actually mean 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". | For example, length is a physical quantity. The metre is a unit of length that [[represents]] a definite predetermined length. When we say 10 metres (or 10 m), we actually mean 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". | ||
| − | The definition, agreement, and [[practical]] use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in [[human]] endeavour from early ages up to this day. Disparate [[systems]] of units used to be very common. Now there is a global [[standard]], the [ | + | The definition, agreement, and [[practical]] use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in [[human]] endeavour from early ages up to this day. Disparate [[systems]] of units used to be very common. Now there is a global [[standard]], the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_System_of_Units International System of Units] (SI), the modern [[form]] of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_system metric system]. The SI has been or is in the [[process]] of being adopted throughout the world. |
| − | In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of [[governmental]] regulation, to ensure [[fairness]] and [[transparency]]. The [ | + | In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of [[governmental]] regulation, to ensure [[fairness]] and [[transparency]]. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bureau_international_des_poids_et_mesures Bureau international des poids et mesures] (BIPM) is tasked with ensuring worldwide [[uniformity]] of measurements and their traceability to the International System of Units (SI). [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metrology Metrology] is the [[science]] for developing national and internationally accepted units of weights and measures. |
In [[physics]] and metrology, units are [[standards]] for measurement of [[physical]] [[quantities]] that need clear definitions to be useful. Reproducibility of [[experimental]] results is central to the [[scientific method]]. A standard system of units facilitates this. Scientific systems of units are a refinement of the [[concept]] of weights and measures [[developed]] long ago for [[Business|commercial]] [[purposes]]. | In [[physics]] and metrology, units are [[standards]] for measurement of [[physical]] [[quantities]] that need clear definitions to be useful. Reproducibility of [[experimental]] results is central to the [[scientific method]]. A standard system of units facilitates this. Scientific systems of units are a refinement of the [[concept]] of weights and measures [[developed]] long ago for [[Business|commercial]] [[purposes]]. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Science]], medicine, and engineering often use larger and smaller units of measurement than those used in everyday life and indicate them more precisely. The judicious selection of the units of measurement can aid researchers in problem solving | [[Science]], medicine, and engineering often use larger and smaller units of measurement than those used in everyday life and indicate them more precisely. The judicious selection of the units of measurement can aid researchers in problem solving | ||
| − | In the [[social sciences]], there are no standard units of measurement and the [[theory]] and [[practice]] of measurement is studied in [ | + | In the [[social sciences]], there are no standard units of measurement and the [[theory]] and [[practice]] of measurement is studied in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychometrics psychometrics] and the theory of conjoint measurement.[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Units_of_measurement] |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*'''''[[Union]]''''' | *'''''[[Union]]''''' | ||
Latest revision as of 02:41, 13 December 2020
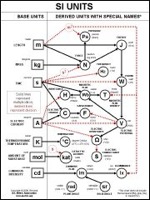
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of measurement.
For example, length is a physical quantity. The metre is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. When we say 10 metres (or 10 m), we actually mean 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre".
The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to this day. Disparate systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. The SI has been or is in the process of being adopted throughout the world.
In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of governmental regulation, to ensure fairness and transparency. The Bureau international des poids et mesures (BIPM) is tasked with ensuring worldwide uniformity of measurements and their traceability to the International System of Units (SI). Metrology is the science for developing national and internationally accepted units of weights and measures.
In physics and metrology, units are standards for measurement of physical quantities that need clear definitions to be useful. Reproducibility of experimental results is central to the scientific method. A standard system of units facilitates this. Scientific systems of units are a refinement of the concept of weights and measures developed long ago for commercial purposes.
Science, medicine, and engineering often use larger and smaller units of measurement than those used in everyday life and indicate them more precisely. The judicious selection of the units of measurement can aid researchers in problem solving
In the social sciences, there are no standard units of measurement and the theory and practice of measurement is studied in psychometrics and the theory of conjoint measurement.[1]